
Greece, an ancient country, officially the Hellenic Republic and historically known as Hellas, is located in Southern and Southeast Europe.
As of 2016, it had a population of 11 million people. It is a country famous for its ancient architecture and famous history. Tourists from all over the world visit this place throughout the year to feel the warmth of antiquity that predominates the air. As much as we are attracted to the structure of this age-old country, very few of us actually try to get to know the roots of this civilisation. Let us then embark on a historical journey and try to get to know a bit about this dated country.
Ancient Greece
Greece is considered to be one of the earliest civilisations of the world and it belongs to a period of Greek history from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th-9th Century BC to the end of the Classical Era (c. AD 600). Greek urban poleis (city-states) began to form in the 8th century BC, approximately the even buries after the Late Bronze Age collapse of Mycenaean Greece. It ushered in the Archaic period and colonisation of the Mediterranean Basin and after that emerged the period of Classical Greece. It was an era which began with the Greco-Persian Wars and lasted from the 5th to 4th centuries BC.
Alexander the Great’s conquests made the Hellenistic civilisation to flourish from Central Asia to the Western end of the Mediterranean Sea. The conquests and annexations of the eastern Mediterranean World by the Roman Republic brought an end to the Hellenistic period.
Classical Greece is often considered the formative ground that provided the foundation of the modern Western culture. It is also considered the cradle of Western civilisation. It gave a lot of importance to knowledge and back in the day also, science and religion were not individual entities. It was considered that getting closer to scientific truth meant getting closer to the Gods.
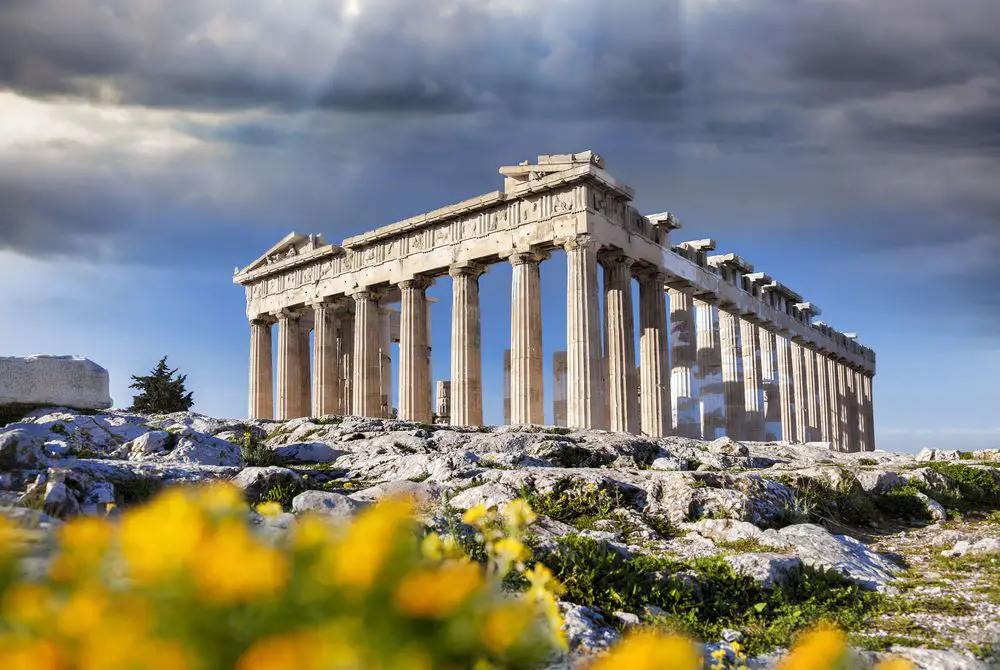

Split into four periods, namely, Archaic, Classical, Hellenistic and Roman, the history of the Greek civilisation proves to be very fascinating.

Emerging from the Dark Ages in the 8th century BC, the Greeks adopted the Phoenician alphabet, having forgotten the Mycenaean script, and modified it to create the Greek alphabet. The earliest evidence of Greek writing comes from Greek pottery graffiti during the 8th century.
A war between the two important poleis of Chalcis and Eretria, called the Lelantine War (c 710-c 650 BC), over the fertile lelantine plain of Euboea, happens to be the earliest documented war of the ancient Greek period.
The introduction of coinage in about 680 BC resulted in the rising of the 7th century BC. This newfound wealth made the merchants desire political power and the aristocracies had to fight in order to not be overthrown by the ‘populist tyrants’.
The democracy that we practice all over the world today was first introduced by the Athenians. Having lost their city-state to Peisistratus and recovered in turn by the Spartan king Cleomenes I, Athens was made into democratic poleis, by the latter, in order to prevent it from being a Spartan puppet. The advent of democracy led to the ‘golden age’ for the Athenians.
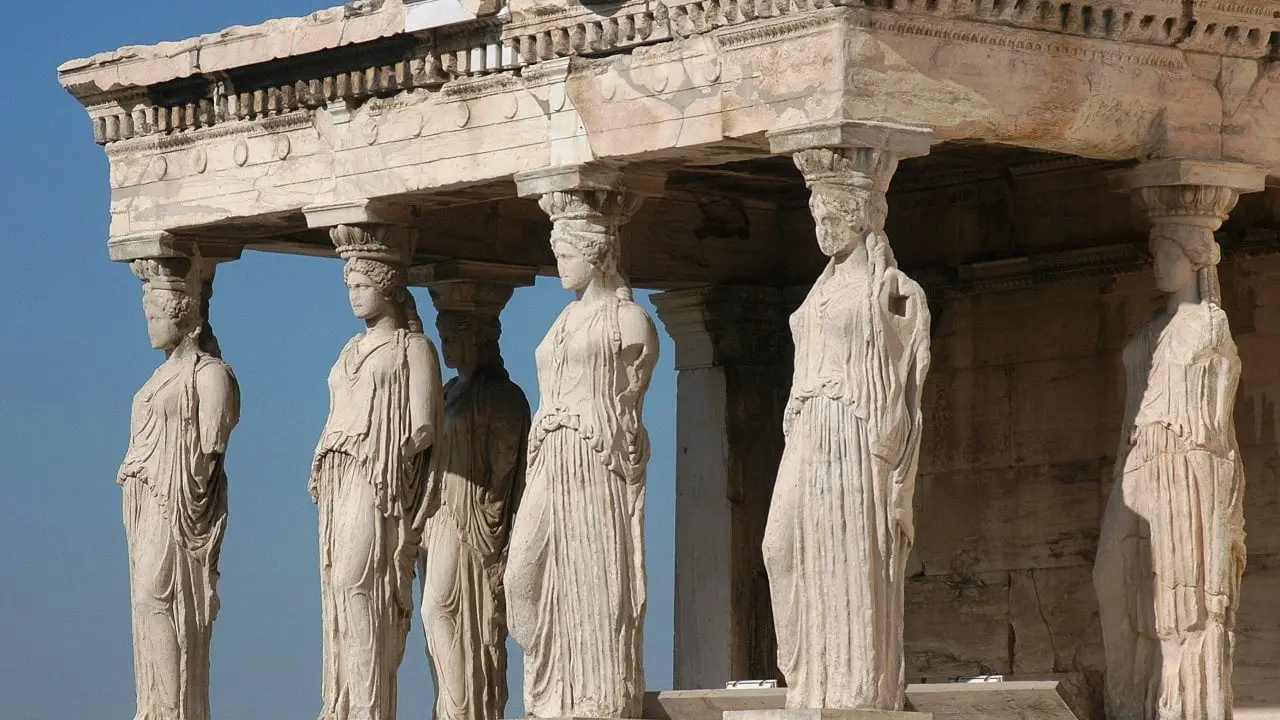

The Greeks were keen administrators of philosophy, which had a large influence on modern philosophy as well as modern day science. Well-known philosophers like Plato, Aristotle and Socrates were the people through whom we can get to know a lot more about the society and politics of those times, e.g. Republic by Plato.
It can undoubtedly be said that ancient Greece was the seat of learning and culture. Western literature and theatre, as we know it today, can be said to have evolved from here. Early Greek poets like Homer, tragedians like Aeschylus, Sophocles and Euripides, Comedian like Aristophanes etc are the ones who were the first ones to give to us the taste of epics, tragedies and comedies. A lot of changes can be seen in the modern day plays but this remains the foundation ground.
The Hellenistic period saw the literary epicentre move from Athens to Alexandria, cultural centres such as Pella and Pergamon came into being. Thanks to the Hellenistic Kings and especially to the Museum of Alexandria that so much of the ancient Greek literature has survived.
Hand in hand with literature went music and dance.
Music was present in every corner of the Greek society, from marriages to funerals to religious ceremonies, theatre, folk music and ballad-like recitation of epic poetry, it was everywhere.
The way the Greek culture embraced literature, music and dance, they welcomed science and technology in the same manner. Ancient Greek mathematicians have made a lot of important developments in the field of mathematics. The discoveries of several Greek mathematicians, like Pythagoras, Euclid and Archimedes are used in the teachings of mathematics even today.
The ancient Greeks have also made important discoveries in the field of medicine. Hippocrates, referred to as the ‘father of medicine’ had lasting contributions to the field as the founder of the Hippocratic School of Medicine. This intellectual school revolutionized medicine in ancient Greece and established it as a discipline distinct from other fields. This, medicine was made into a profession.

The ancient Greek art and architecture has given us lots of excuses to visit the country time and again just to set eyes on the aesthetic beauty of these age-old ancient structures and monuments. It influenced the art of the Western world in an enormous way. Well into the 19th century, the classical tradition derived from Greece dominated the art of the Western world.
No matter how advanced the science and technology of those days were, it could not remove the people from religion and mythology because, as said earlier, these two were not treated as separate or competing entities. Their religious practices gave way to beautiful art forms, especially in literature, and these myths and legends were the steppingstones for the Western literature to develop into what it is today.

The civilisation of ancient Greece has immensely influenced the language, politics, educational system and others. Via the Roman Empire, the Greek culture came to be the foundation of the Western culture in general. A modern revival of Classical Greek learning took place in the Neoclassicism movement in 18th and 19th century Europe and Americas.
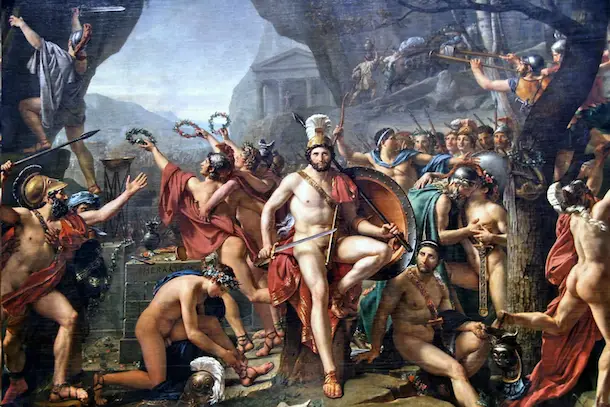

The advanced ‘ancient’ civilisation of Greece was the foundation ground for culture in forms of art, literature religion and science. As mentioned earlier, it was also the first country to have a democratic city-state. So, How ancient is it really? Is it ancient at all? Think about it.
Read Also: Greek Mythology: Off Stories, Legends and Tragedies.



